| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- 프로그래머스
- VirtualTryON
- video generation
- Programmers
- flow matching
- ddim inversion
- Python
- Machine Unlearning
- unlearning
- inversion
- image editing
- video editing
- rectified flow
- flow models
- diffusion model
- 코테
- diffusion models
- 3d editing
- 3d generation
- BOJ
- diffusion
- rectified flow matching models
- 네이버 부스트캠프 ai tech 6기
- rectified flow models
- 논문리뷰
- image generation
- flow matching models
- visiontransformer
- Concept Erasure
- memorization
- Today
- Total
평범한 필기장
[평범한 학부생이 하는 논문 리뷰] UniEdit-Flow : Unleashing Inversion and Editing in the Era of Flow Models (arXiv 2504) 본문
[평범한 학부생이 하는 논문 리뷰] UniEdit-Flow : Unleashing Inversion and Editing in the Era of Flow Models (arXiv 2504)
junseok-rh 2025. 4. 27. 23:53Paper : https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.13109
UniEdit-Flow: Unleashing Inversion and Editing in the Era of Flow Models
Flow matching models have emerged as a strong alternative to diffusion models, but existing inversion and editing methods designed for diffusion are often ineffective or inapplicable to them. The straight-line, non-crossing trajectories of flow models pose
arxiv.org
Abstract
Diffusion model을 위해 디자인된 inversion과 editing method들은 flow model들에 대해서는 비효율적이거나 적용할 수 없다. 그래서 본 논문에서는 flow model들에서 inversion과 editing을 위한 predictor-corrector-based framework을 도입한다. 본 논문은 정확한 reconstruction을 위한 효과적인 inversion method인 Uni-Inv를 제안한다. 그리고 region-aware이고 robust한 image editing method인 Uni-Edit을 도입한다.

1. Background
1.1 Delayed Injection
기존 연구들은 editing 동안에 image consistency를 유지하도록하는 delayed injection을 도입했다. 이는 특정 timestep 전에 original condition들을 유지하거나 inversion process로부터의 latent representations를 재사용하고, 그 후에 editing condition들을 주입한다. 이는 content preservation과 targeted modification사이의 균형잡힌 trade-off를 가능하게 한다.

Diffusion model의 non-linear이고 교차하는 sampling trajectory 때문에, 중간에 condition을 수정하는 것은 trajectory transition을 가능하게 하고, 이는 더 유연하고 localized image editing을 용이하게 한다. 그러나, flow model은 straight-line이고 non-intersecting trajectory를 가지는데, 이는 특히 image editing에서 delayed injection의 효율성을 방해한다.
2. Method
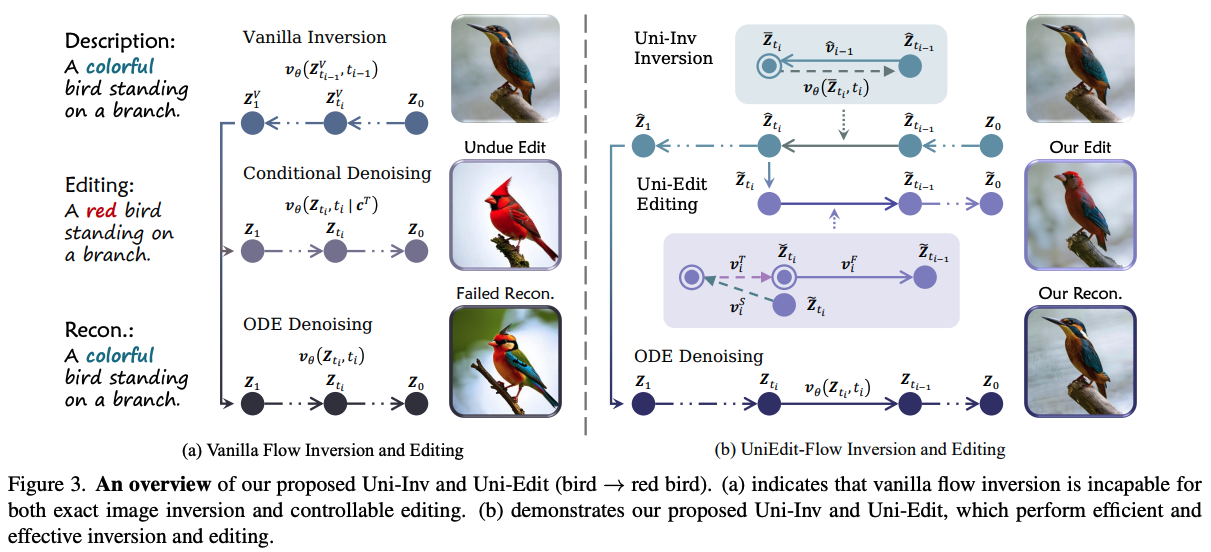
Fig 3(a)에서 각 forward step에서 $\mathbf{Z}$와 $t$ 사이의 mismatch 때문에, reconstructed image와 original image 사이의 consistency를 direct inversion이 보장하는 것은 어렵다. Fig 3(b)에서 본 논문은 predictor-corrector idea를 구현한다.
2.1 Uni-Inv
Uni-Inv의 동기는 initial value로 ODE solution을 inverting해서 정확한 inversion을 수행하는 것이다. 다음 수식을 통해 반복적으로 generation 과정을 거친다.
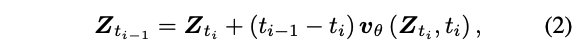
위 수식을 통해서 inverted latent $\mathbf{Z}_{t_i}$의 값을 다음과 같이 구할 수 있다.

그러나, inversion process에서 $\mathbf{Z}_{t_i}$의 값을 알 수 없기 때문에 (3)에서 $v_\theta(\mathbf{Z}_{t_i}, t_i)$를 알 수 없다. 이전의 방식에서는 $v_\theta(\mathbf{Z}_{t_{i-1}}, t_{i-1})$로 근사를 했다. 이 방식은 model prediction이 timestep동안에 consistent하다는 가정을 하는데, 이는 필연적으로 error를 가진다. 본 논문은 inversion step에서, $t_i$에서 $\hat{\mathbf{Z}}_{t_{i-1}}$의 local target에 대응하는 inversion step $v_\theta(\hat{\mathbf{Z}}_{t_{i-1}}, \cdot)$를 evaluate하는 것이 $t_{i-1}$에서 evaluate하는 것보다 정확한 velocity를 생성한다는 것을 보인다.
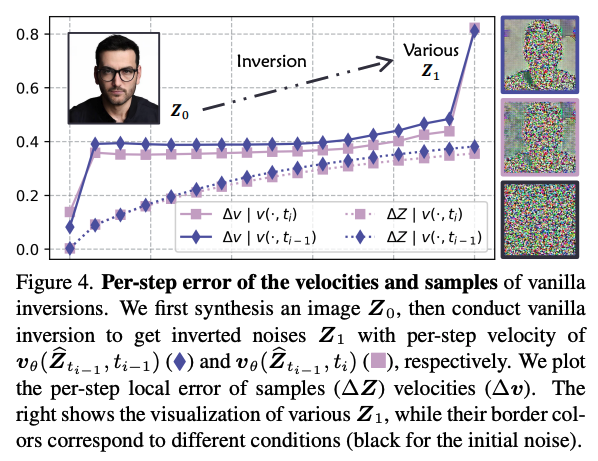
위에서 볼 수 있듯이, $v_\theta(\hat{\mathbf{Z}}_{t_{i-1}}, t_{i-1})$가 $v_\theta(\hat{\mathbf{Z}}_{t_{i-1}}, t_i)$보다 더 큰 local error를 보인다. 그리고 mismatched background를 가진 다른 noise를 reconstruction한다. 두 방식의 error accumulation은 사소하지 않다. 그래서 효과적인 image inversion과 reconstruction의 key는 $t_i$와 $t_{i-1}$에서 velocity field들을 align해서 $\mathbf{\hat{Z}}_{t_{i-1}}$를 통해 $\mathbf{\bar{Z}}_{t_i}$를 찾는데 있다.
적절한 $\bar{\mathbf{Z}}_{t_i}$를 추정하기 위해서, 본 논문은 현재의 time step에서 이전에 얻은 velocity $\bar{\mathbf{v}}_{i-1}$를 재사용하는 것을 제안한다. 먼저 $t_{i-1}$에서 $t_i$로 sample을 backtrack하기 위해서 이 velocity를 이용한다. 그러고 나서 다음 inversion step을 위해, $t_i$와 더 align이 잘 되는 $\hat{\mathbf{v}}_{i-1}$를 계산한다.

Uni-Inv의 전체 알고리즘이다.

위는 reconstruction에 대한 Uni-Inv의 quality에 대한 이론적인 보장을 제공한다.
2.2 Uni-Edit

Direct Edit은 기존과 많이 다른 결과를 발생시키고, delated injection은 기존에서 많이 변하지 않아 미완성인 결과를 보인다. 그래서 이 문제를 해결하기 위해, 본 논문은 current latent $\tilde{\mathbf{Z}}_{t_i}$에 대해서만 기초해 editing 절차 동안 추가적인 correction step을 제안한다. Source condtion $c^S$와 target condition $c^T$에 대해, velocity estimate $v^S_i,v^C_i$를 구한다. Correction step을 도입하기 위해서, $\tilde{\mathbf{Z}}_{t_i}$가 $v^S_i$에 따라 더 높은 noise를 가진 이전의 step으로 먼저 transition된다. 그 후에, $v^C_i$를 통해 $\check{\mathbf{Z}}_{t_i}$로 다시 mapping된다. 이 predictor-corrector 절차는 효과적인 editing을 방해하는 undesirable component를 수정한다. 최종적으로 latent를 $\tilde{\mathbf{Z}}_{t_{i-1}}$로 이동시키기 위해서 current editing velocity를 적용한다.
2.3 Region-Adaptive Guidance and Velocity Fusion
기존 연구는 다른 prompt에 대해 condition된 latent들 사이의 차이는 editing에 중요한 region을 강조한다는 것을 관찰했다. 본 논문은 mask $m_i = \text{MASK}(v^-_i)$를 구성하기 위해서 이 차이 $v^-_i$를 이용한다. 먼저 weighting factor $(1 + m_i)$를 적용해서, edit-relevant region을 더 큰 폭으로 backtrack하게 해서 의도된 수정에 중요한 original concept의 제거를 강화한다. 그 후의 sample update에 대해서 target과 source velocity를 $m_i, (1-m_i)$를 이용해서 fusion한다. 이는 edit-irrelevant region을 상당히 unmodified하게해, 과도한 변화를 막는다.
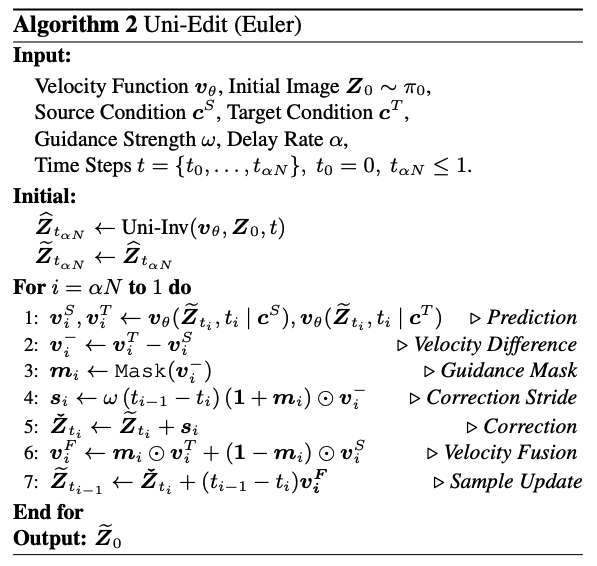
Delayed injection은 background detail을 보전하는 것과 효과적인 수정을 달성하는 것 사이의 balance를 맞추고 inference cost를 줄인다.
3. Experiments
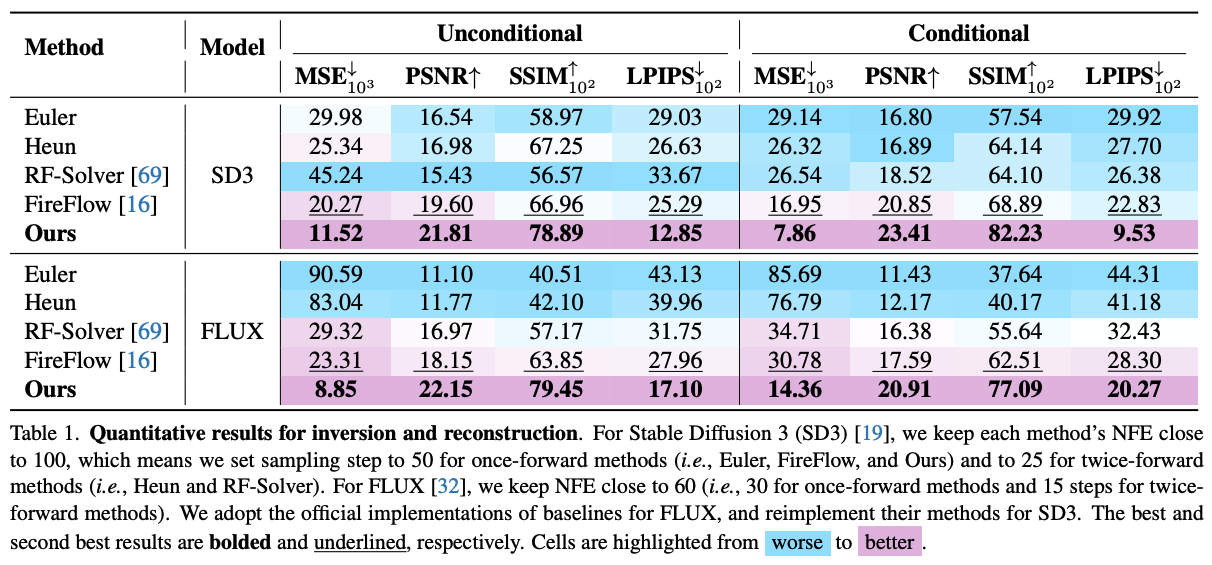
3.1 Real Image Inversion & Reconstruction

3.2 Text-driven Image Editing



3.4 Applications





